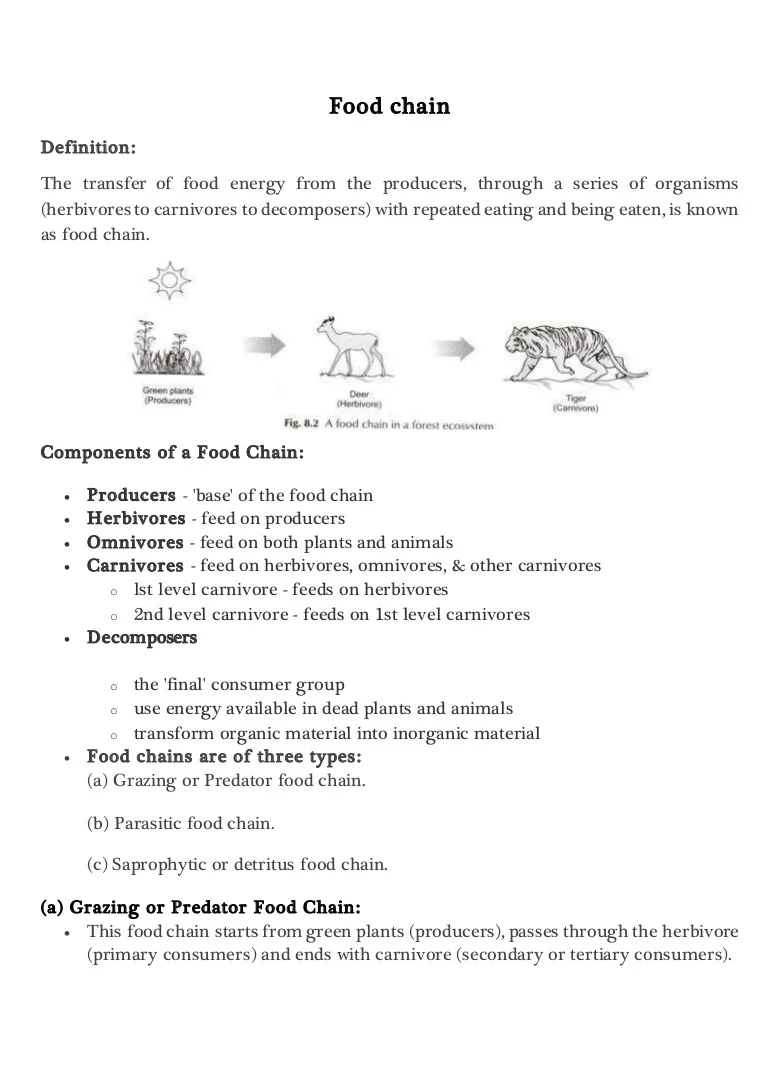
Food Chain Definition Ecology

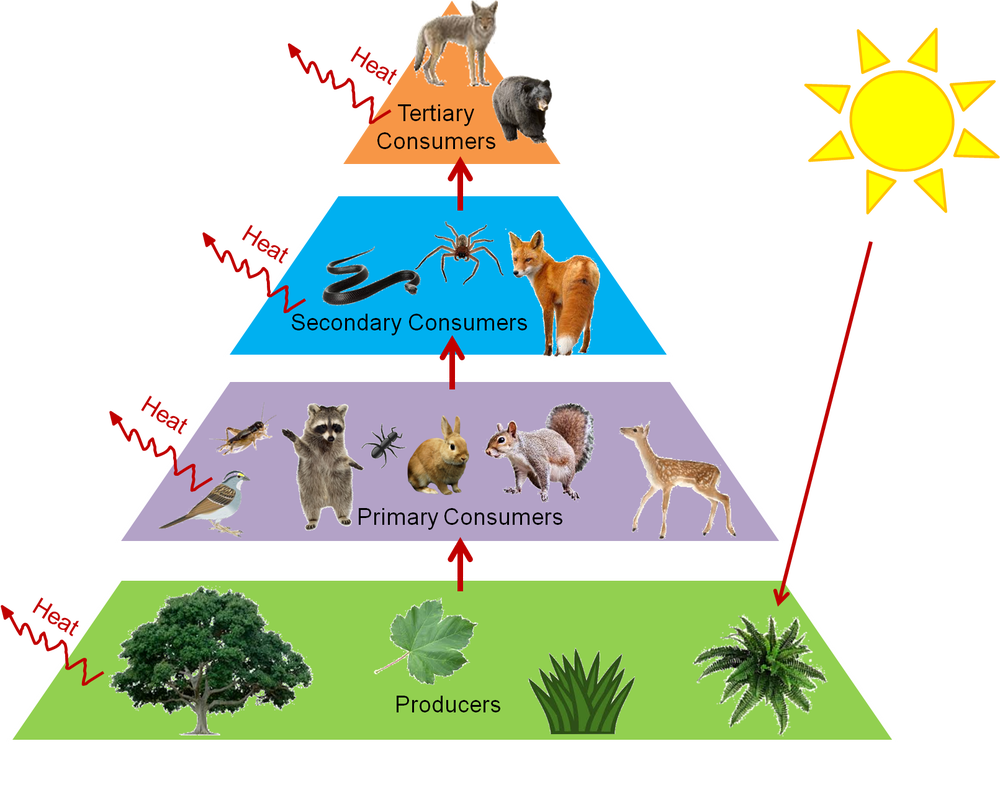
The producers in a food chain include all green plants.
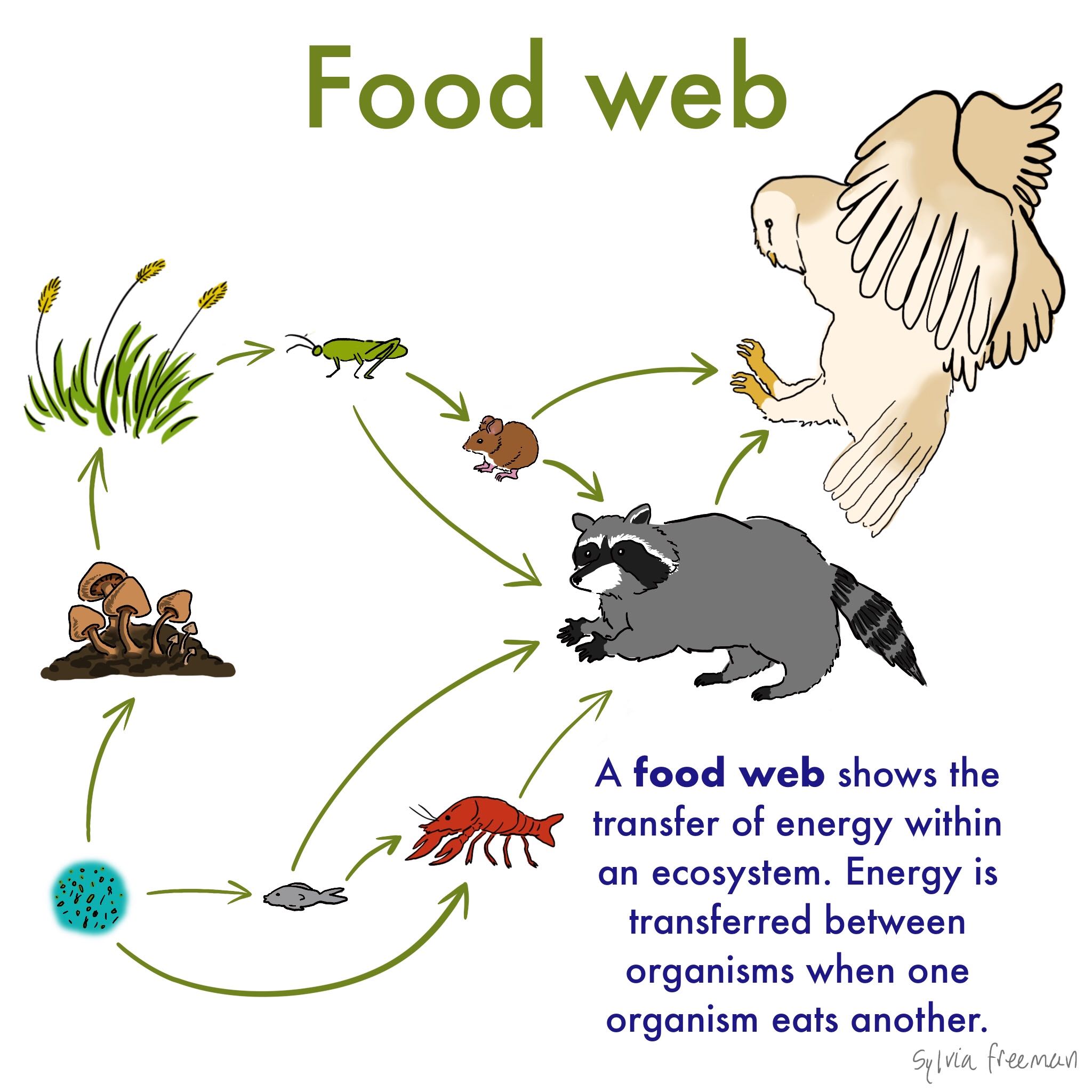
Food chain definition ecology. Food Chains - BrainPOP. In scientific terms a food chain is a chronological pathway or an order that shows the flow of energy from one organism to the other. English 1775114 1977 briefly itemized the stages of two food chains one terrestrial one aquatic Egerton 2007a.
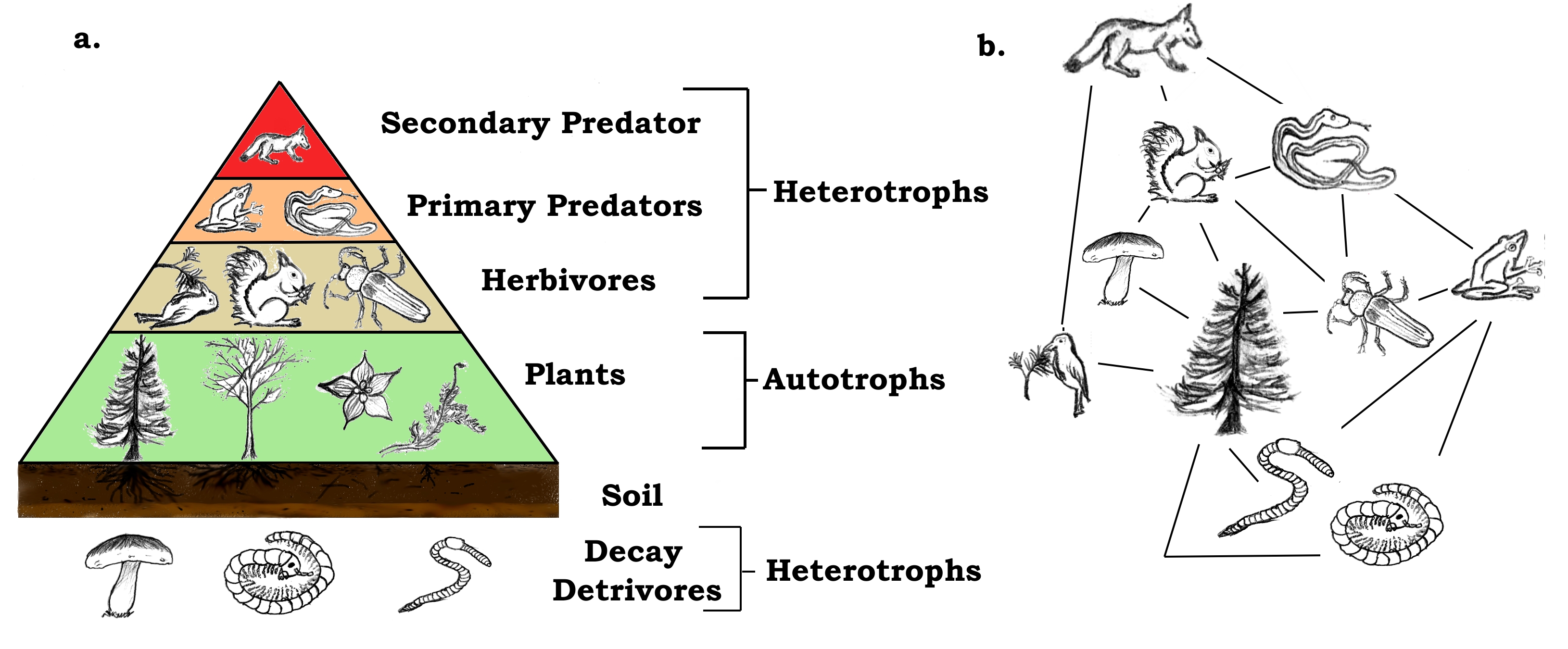
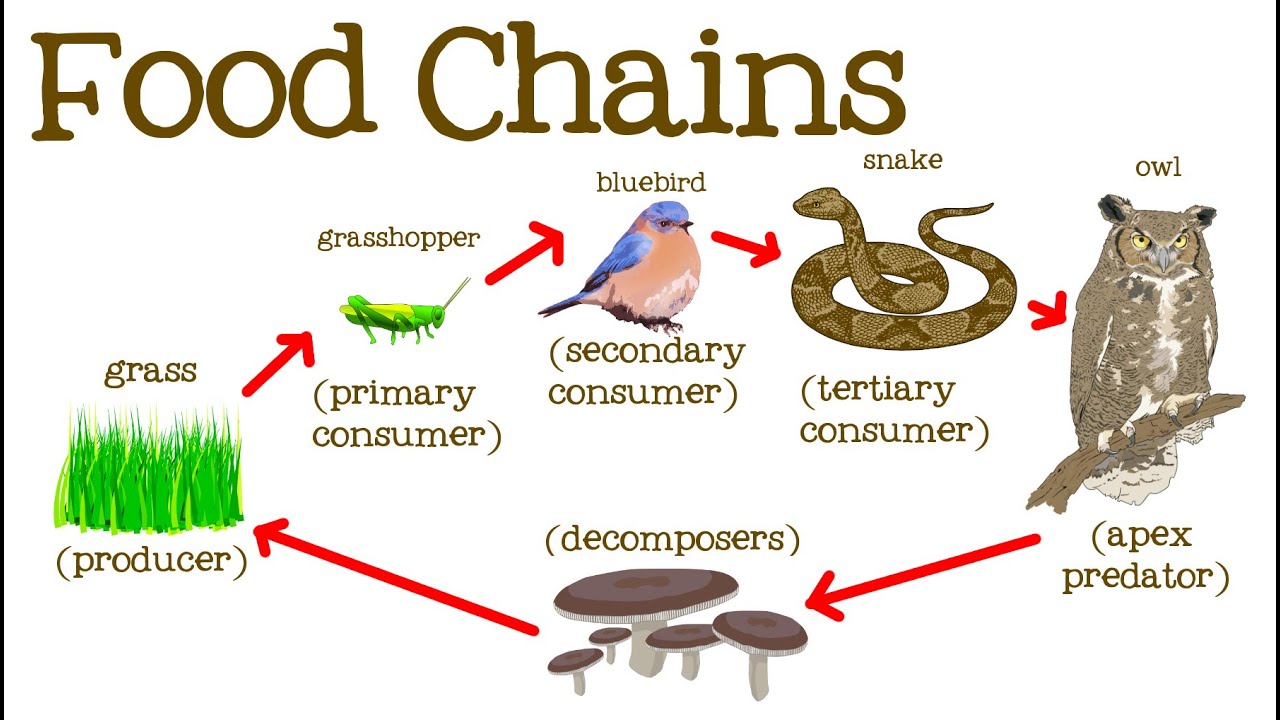
There are likely other naturalists between Linnaeus and Darwin who reported on food chains but attracted little notice. A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web starting from producer organisms such as grass or trees which use radiation from the sun to make their food and ending at apex predator species like grizzly bears or killer whales detritivores like earthworms or woodlice or decomposer species such as fungi or bacteriaa food chain also shows how the organisms. In a community which has producers consumers and decomposers the energy flows in a specific pathway.
The sequence of organism through which the energy flows is known as food chain. For example grass produces its own food from sunlight. From the examples given above we can understand that how the food material forms consumers of different levels of the food chain based on producers.
The food chain is an ideal representation of flow of energy in the ecosystem. Weve got you covered. A food chain is basically made up of producers and consumers.
The sun is the initial source of energy which provides energy for everything on the planet. In ecology a food chain is a series of organisms that eat one another so that energy and nutrients flow from one to the next. Every living thingfrom one-celled algae to giant blue whale sneeds food to survive.
Find the Food Chain Definition Ecology including hundreds of ways to cook meals to eat. Food ecology is the science which looks at the food production process and assesses the impact each stage of the process has on how plants and animals relate. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred from one organism to the other.