Food Chain Definition Class 10

If occupies an intermediate trophic position between primary and secondary consumers.
Food chain definition class 10. Class 10 Biology Our EnvironmentFood chains. The linear sequence of organisms where one is consumed by the other for food is known as a food chain. The food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where nutrients and energy is transferred food chain and food web definition diagram examples videos.
Have students brainstorm different biotic factorsorganisms plants and animals found in either a freshwater or marine ecosystem. A food chain is a series of organisms where all the organismsare dependent on next organism as a source of food. Fundamentally the food chain is the sequence of organisms where the transfer of matter and energy takes place in the form of food from organism to organism.
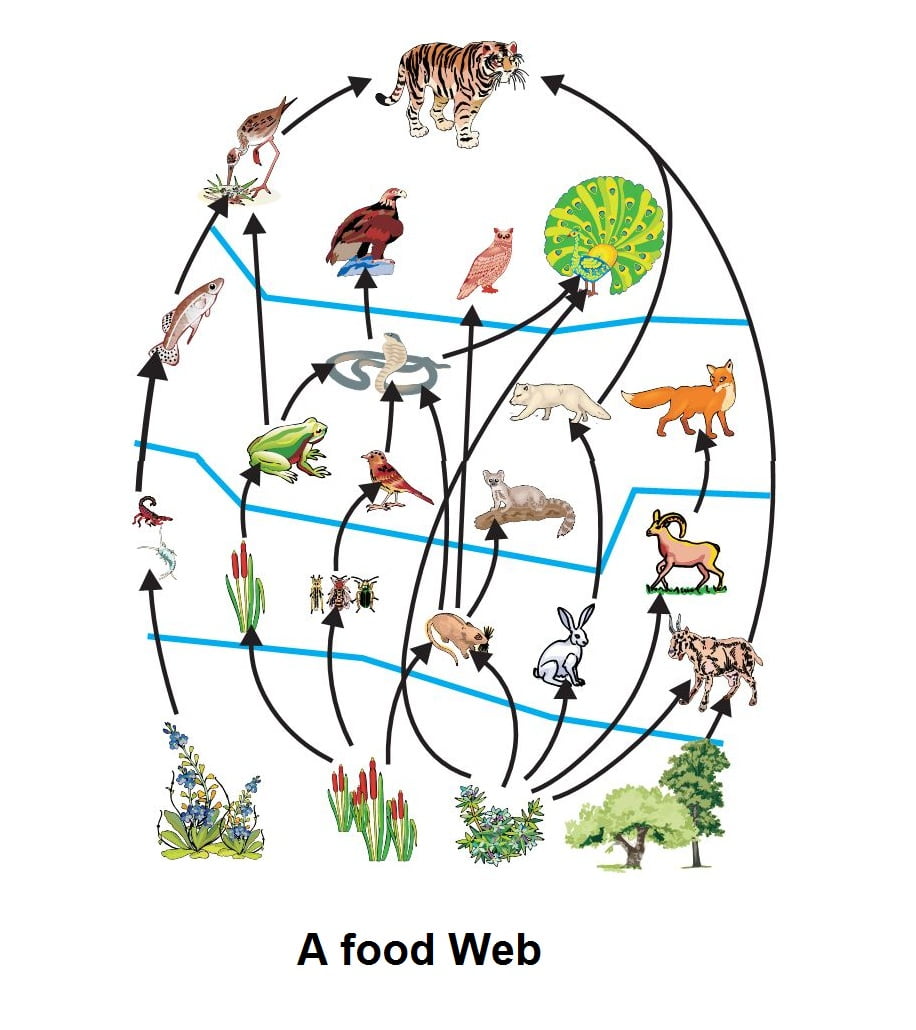
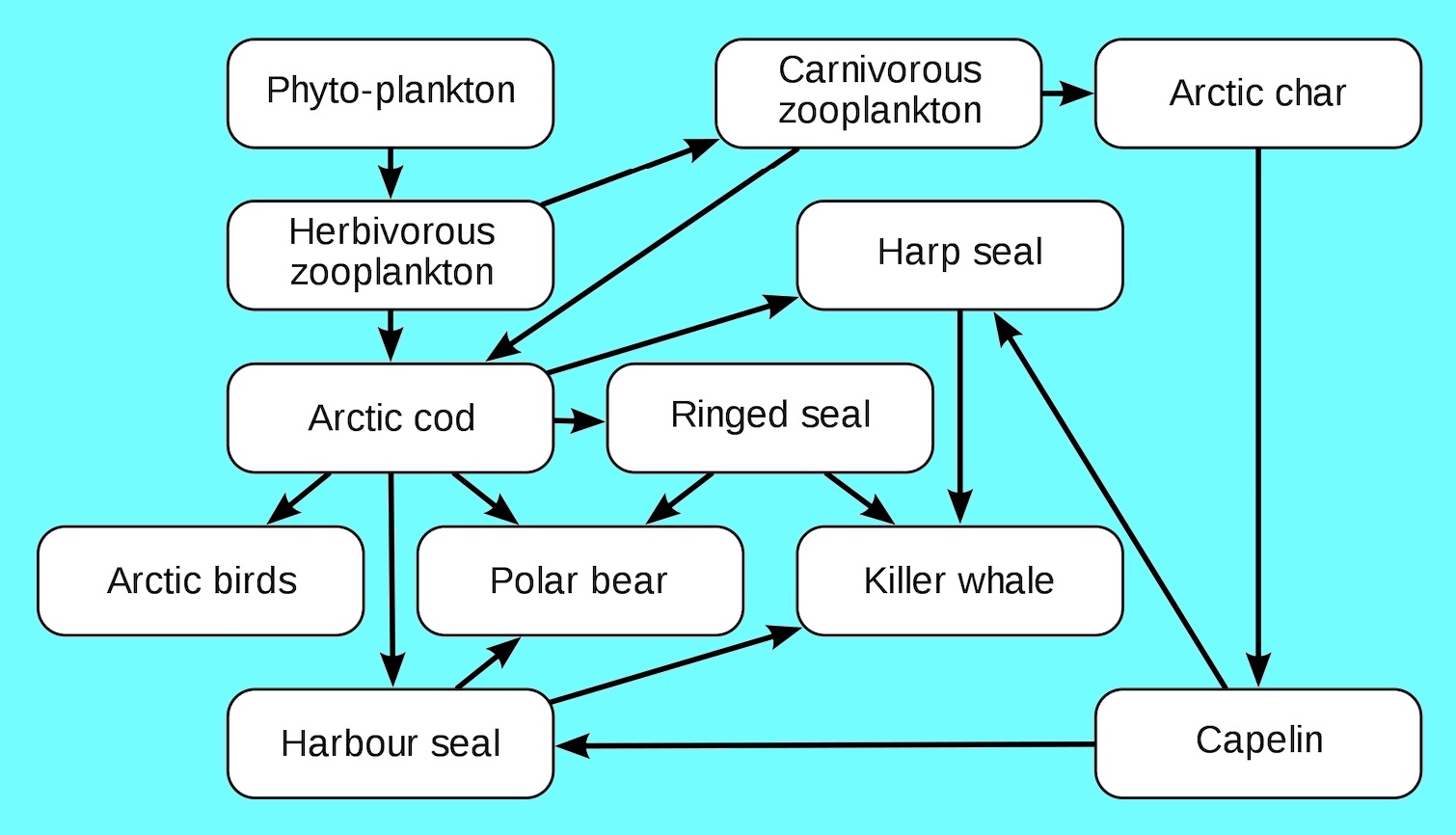
What are Food chains and Explain their Characteristics. A food chain refers to the order of events in an ecosystem where one living organism eats another organism and later that organism is consumed by another larger organism. The definition of food web is a model of food chains that intersect and show what eats what.
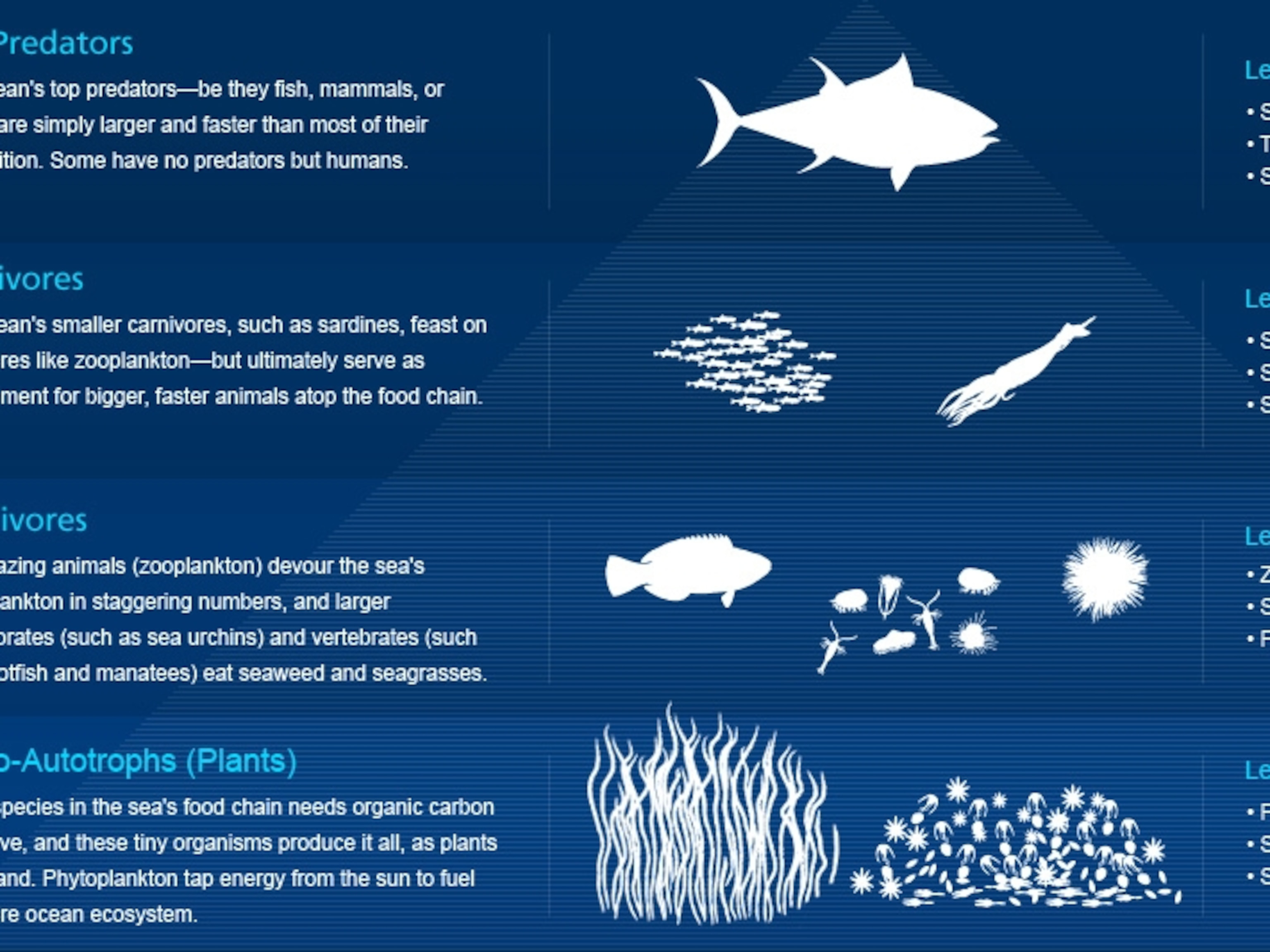
A food chain usually consists of producers various. Food webs are important tools in understanding that plants are the foundation of all ecosystems and food chains. The gradual accumulation of harmful non biodegradable and chemical substances from one trophic level to next trophic level and then throughout The food chain is known as biological magnification.
In a community which has producers consumers and decomposers the energy flows in a specific pathway. Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. Food chains are more or less familiar to everyone in a vague sort of way.
In scientific terms a food chain is a chronological pathway or an order that shows the flow of energy from one organism to the other. Usually there are 3 or 4 trophic levels in the food chain. The series of organism take part at various biotic levels to form a food chain.