Cellular Respiration Meaning In Biology

Aerobic respiration requires oxygen to fully oxidise the organic molecule.
Cellular respiration meaning in biology. Autotrophs like plants produce glucose during photosynthesis. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form.
But cellular respiration is slightly more complicated than just converting the energy from glucose into ATP. Cellular respiration Cellular respiration n. Both aerobic and anaerobic respiration involve chemical reactions which take place in the cell to produce energy which is needed for active processes.
In this process glucose breaks down without the help of oxygen and the by-products produced are alcohol CO2 and energy or ATP. Cellular respiration stores chemical energy in the form of phosphorylated nucleotides primarily ATP by means of oxidative reactions and makes it available to other reactions. Other types of organisms such as animals fungi many protozoa and a large.
Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism. Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in all living cells to release energy by converting biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate- ATP.
Signal transduction The transmission of signals from a cells outside to its inside. The principal carbohydrate formed through photosynthesis is glucose. Cellular respiration can be described as the reverse or opposite of photosynthesis.
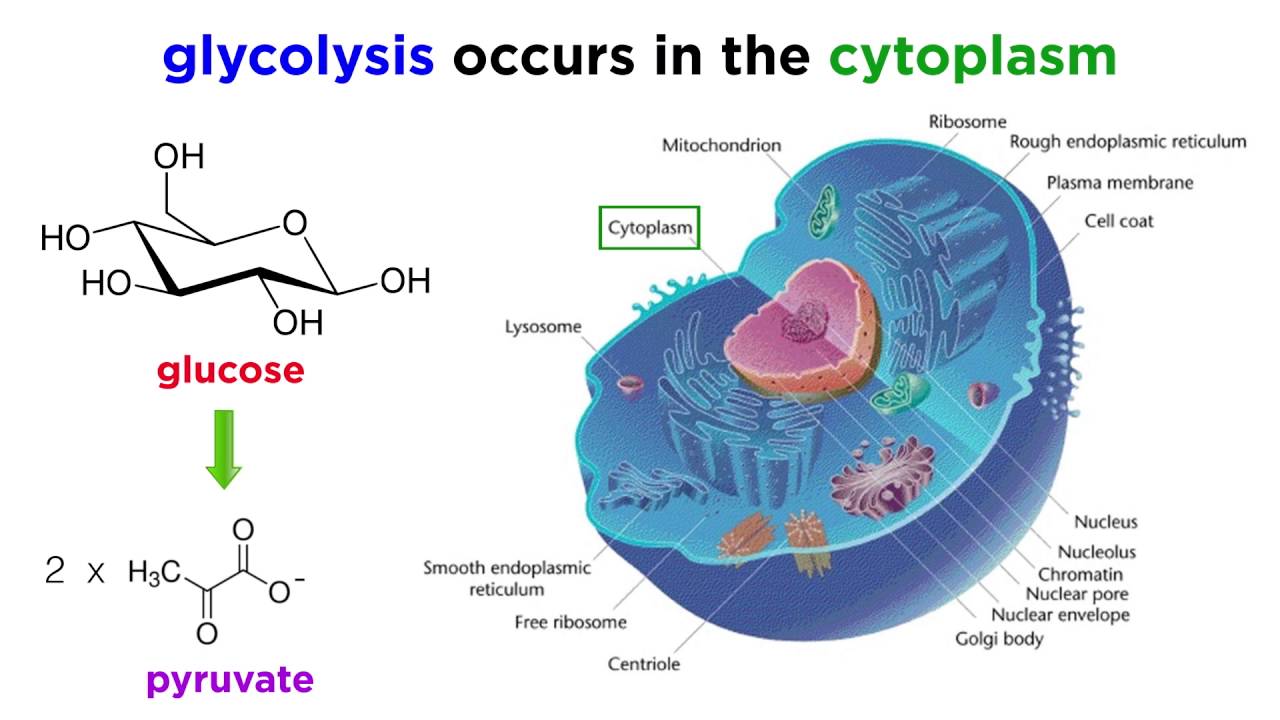
The process plays an essential role in maintaining the biological functions of all living cells. Cellular respiration the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding as waste products carbon dioxide and water. Glycolysis is the first step in the breakdown of glucose to extract energy for cellular metabolism.