Cell Membrane Structure And Function A Level

The Formation of Cell Membranes is Crucial to Life.
Cell membrane structure and function a level. Contains chromosomes DNA code for the synthesis of proteins that control the function of the cell hence the nucleus commands the cell Cell Surface membrane. Some of these proteins span the whole width of the membrane. Xylem present in the vascular plants is made of cells that provide structural.
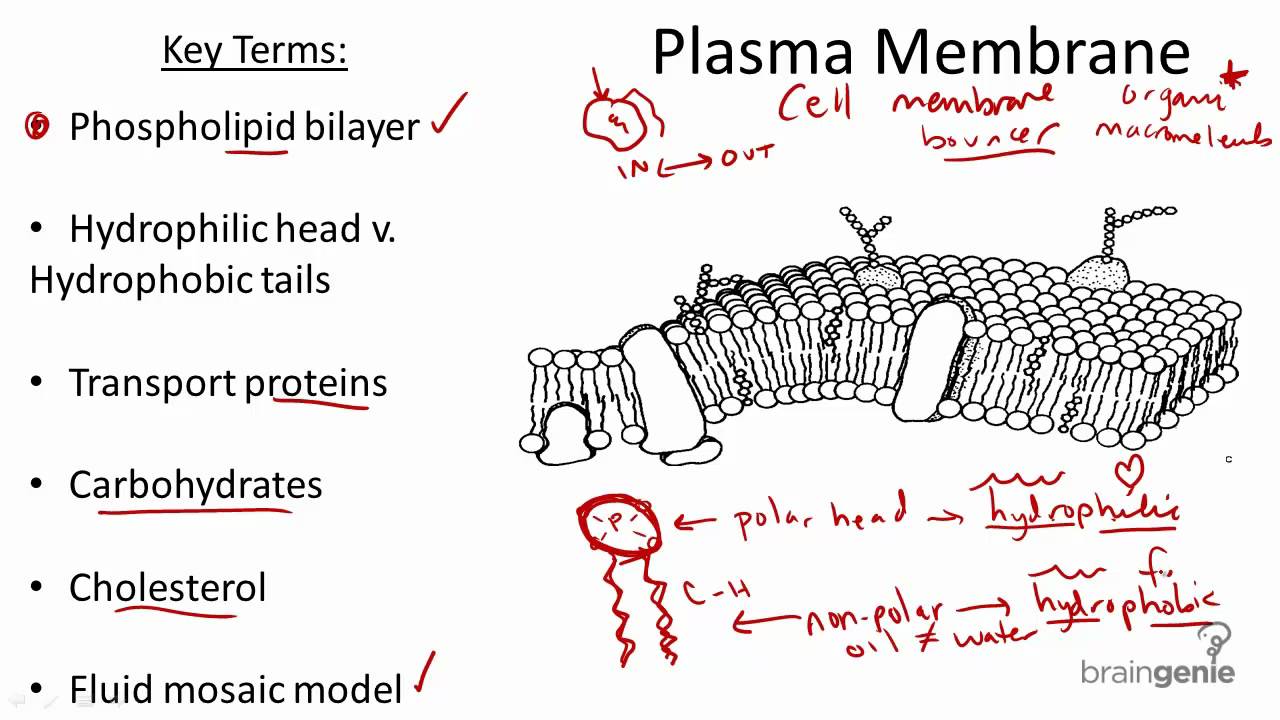
1 Isolate cells contents from outside environment 2 Regulate exchange of substances between inside and outside of cell 3 Communicate with other cells Note. It is a fluid mosaic of lipids proteins and carbohydrate. Membrane Structure and Function Plasma Membrane.
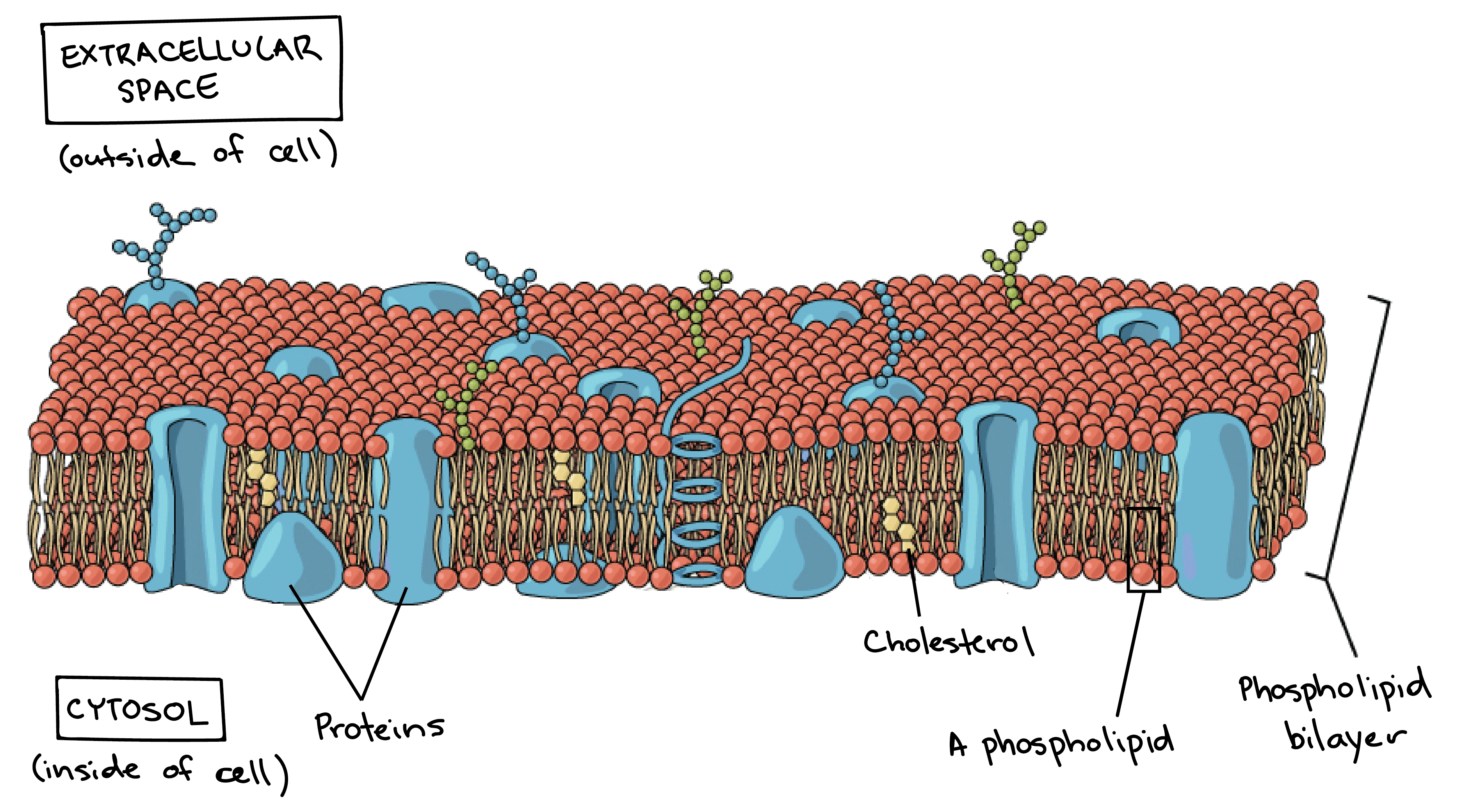
The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer including cholesterols that sit between phospholipids to maintain their fluidity at various temperatures. Organelles perform different functions within a cell and this is called the Division of Labour. The cell membrane is a multifaceted membrane that envelopes a cells cytoplasm.
Different organelles have distinct structures and functions. All membranes in a cell have the same basic structure which compartmentalises organelles from its external environment. All cells are surrounded by the cell membranes and this characteristic best portrayed by the Fluid Mosaic ModelAccording to this model which was postulated by Singer and Nicolson during the 1970s plasma membranes are composed of lipids proteins and carbohydrates that are arranged in a mosaic-like manner.
Structure of Plasma Membrane The plasma membrane also known as the cell membrane or cytoplasmic membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of a cell from its outside environment. The fundamental structure of the plasma membrane. The cell wall and the cell membrane are the main components that function to provide support and structure to the organism.
Much of the membrane is made up of a sea of phospholipids with protein molecules floating in between the phospholipids. Act as a barrier to most water-soluble substances the non-polar fatty acid tails prevent polar molecules or ions from passing across the membrane. It protects the integrity of the cell along with supporting the cell and helping to maintain the cells shape.